Mastering the Art of Flat Roof Insulation: A Comprehensive Guide
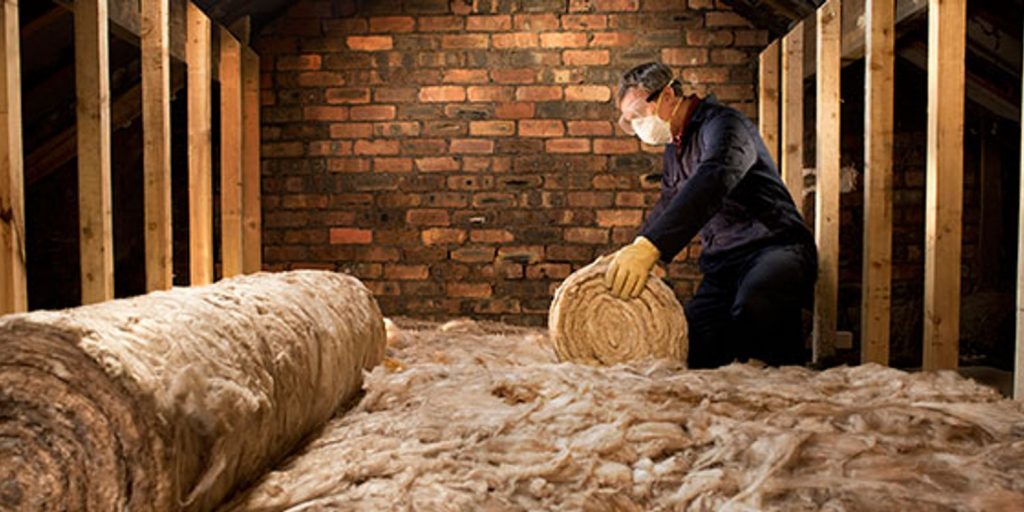

Insulating a flat roof is a crucial step in ensuring energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and protection against the elements. Whether you're constructing a new building or renovating an existing one, understanding the ins and outs of flat roof insulation is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various techniques, materials, and considerations involved in insulating a flat roof.
- Assessing the Roof Structure:
Before diving into insulation, it's important to assess the roof structure. Flat roofs can be constructed using different materials, such as concrete, metal, or timber. Understanding the specific characteristics of your roof will help determine the most suitable insulation approach. - Choosing the Right Insulation Material:
There are several insulation materials available for flat roofs, each with its own advantages and considerations. These include: a. Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Insulation: PIR boards offer excellent thermal performance and moisture resistance, making them a popular choice for flat roofs. They are lightweight, easy to install, and provide high insulation values. b. Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Insulation: XPS boards are known for their high compressive strength and moisture resistance. They are ideal for areas with high foot traffic or where water infiltration is a concern. c. Mineral Wool Insulation: Mineral wool provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties. It is a versatile material that can be used in various roof types, including flat roofs. d. Spray Foam Insulation: Spray foam insulation offers seamless coverage, filling gaps and voids effectively. It provides superior thermal insulation and can also act as a vapor barrier. - Understanding Insulation Techniques:
Insulating a flat roof requires careful consideration of the insulation technique to ensure optimal performance. Some common techniques include: a. Warm Roof Insulation: In this technique, insulation is installed above the roof deck, keeping the structural elements warm. It helps prevent condensation and thermal bridging. b. Cold Roof Insulation: Cold roof insulation involves placing insulation between the roof joists, allowing the roof deck to remain cold. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent moisture buildup. c. Inverted Roof Insulation: This technique places the insulation layer above the waterproofing membrane. It protects the membrane from temperature fluctuations and provides additional thermal mass. - Addressing Thermal Bridges:
Thermal bridges can significantly impact the effectiveness of flat roof insulation. These are areas where heat can escape or enter the building more easily, leading to energy loss. Proper insulation installation, such as using insulation boards with tongue and groove joints, can help minimize thermal bridging. - Vapor Barriers and Air Sealing:
To prevent moisture buildup and ensure long-term durability, installing a vapor barrier is essential. It helps control the movement of moisture through the roof assembly. Additionally, proper air sealing techniques, such as sealing gaps and joints, are crucial to maintain the insulation's effectiveness.
Conclusion:
Insulating a flat roof is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. By understanding the roof structure, choosing the right insulation material, employing suitable techniques, addressing thermal bridges, and ensuring proper vapor barriers and air sealing, you can achieve a well-insulated flat roof that enhances energy efficiency and provides optimal thermal comfort.