Unveiling the Distinction: Exterior Cladding vs. Facade
In the realm of architecture and construction, the terms "exterior cladding" and "facade" are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion among professionals and enthusiasts alike. However, understanding the subtle yet significant differences between these two concepts is crucial for creating aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound buildings. In this blog post, we will delve into the depths of exterior cladding and facade, unraveling their distinctions and shedding light on their respective roles in architectural design.
- Defining Exterior Cladding:
Exterior cladding refers to the protective layer or covering applied to the exterior walls of a building. It serves as a shield against environmental elements, enhancing insulation, weather resistance, and durability. The primary purpose of exterior cladding is to safeguard the underlying structure while providing an aesthetic appeal. Common materials used for cladding include wood, metal, stone, fiber cement, and composite materials. - Exploring Facade:
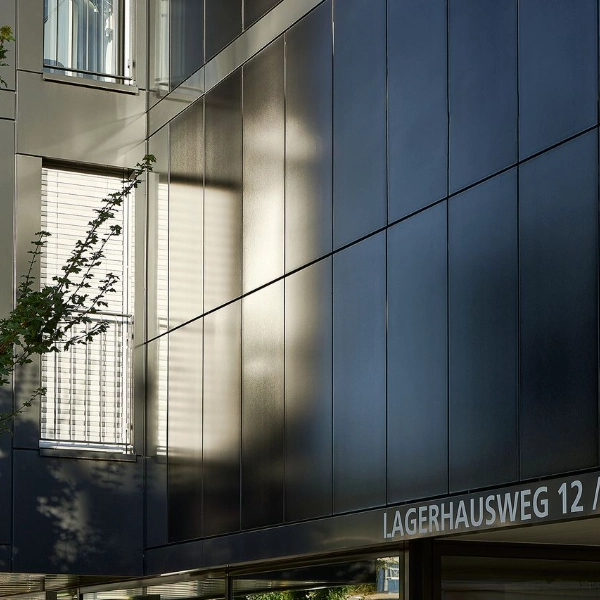
Facade, on the other hand, encompasses the entire front-facing exterior of a building, including the cladding, windows, doors, and any other architectural elements. It represents the visual identity and character of a structure, often reflecting the design style or era it belongs to. While exterior cladding is a component of the facade, the facade encompasses a broader scope, incorporating various design elements and architectural features. - The Relationship between Exterior Cladding and Facade:
Exterior cladding plays a vital role in shaping the facade of a building. It acts as the outermost layer, contributing to the overall appearance and style. The choice of cladding material, color, texture, and installation technique significantly influences the visual impact of the facade. However, the facade encompasses additional elements such as windows, doors, balconies, and decorative elements, which collectively define the building's architectural character. - Functionality vs. Aesthetics:
While both exterior cladding and facade contribute to the visual appeal of a building, they serve distinct purposes. Exterior cladding primarily focuses on functionality, providing protection against weather conditions, moisture, and structural damage. On the other hand, the facade emphasizes aesthetics, creating an inviting and visually striking exterior that reflects the building's purpose, cultural context, or design intent. - Integration and Harmonization:
Achieving a harmonious relationship between exterior cladding and facade is crucial for successful architectural design. The cladding material should complement the overall facade design, blending seamlessly with other architectural elements. The choice of colors, textures, and patterns should align with the building's purpose, surrounding environment, and desired visual impact. A well-integrated exterior cladding and facade can elevate the building's aesthetics and contribute to its longevity.
Conclusion:
In summary, while exterior cladding and facade are closely related, they possess distinct roles in architectural design. Exterior cladding primarily focuses on functionality and protection, while the facade encompasses a broader range of design elements, including cladding, windows, doors, and decorative features. Understanding the differences between these concepts is essential for architects, designers, and construction professionals to create visually appealing and structurally sound buildings that stand the test of time.