What Are Thermal Pads and How Do They Improve Heat Dissipation
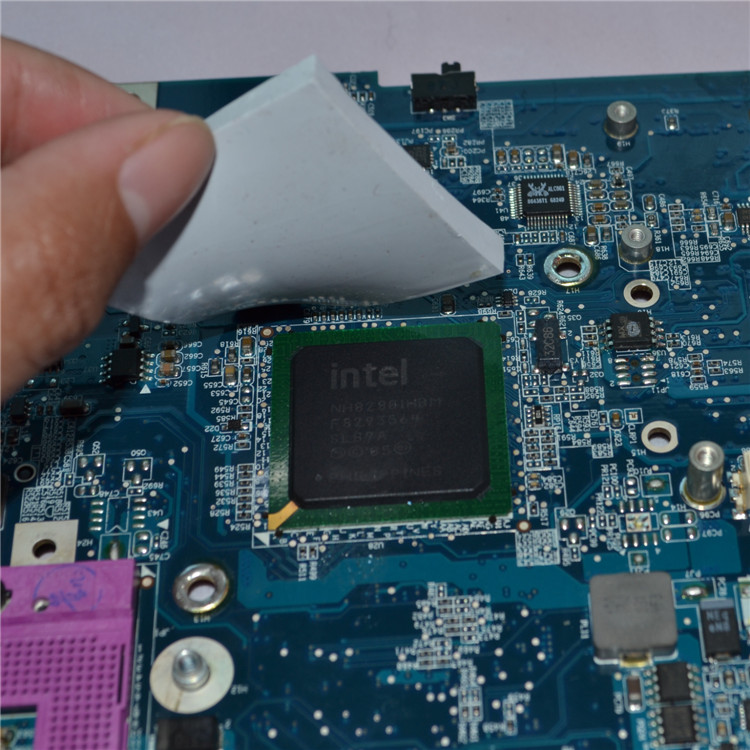

Thermal pads are widely used across consumer electronics, industrial equipment, automotive systems, and power electronics. Companies like Dubang Materials focus on developing reliable thermal interface materials that meet the real-world demands of modern thermal management. To understand their value, it’s important to first look at what thermal pads are and how they improve heat dissipation in practical applications.
What Are Thermal Pads?
Thermal pads, also known as thermal interface pads, are soft, heat-conductive materials placed between heat-generating components and heat-dissipation surfaces such as heat sinks, metal housings, or chassis frames. Their main function is to fill microscopic air gaps between uneven surfaces.
Even surfaces that appear smooth to the naked eye contain tiny imperfections. When two solid parts are placed together, these gaps trap air, which is a poor conductor of heat. Thermal pads displace air and create a continuous thermal pathway, allowing heat to transfer more efficiently.
Most thermal pads are made from silicone-based elastomers combined with thermally conductive fillers. Depending on application needs, they may include additional reinforcement layers, such as fiberglass, to improve mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
How Thermal Pads Improve Heat Dissipation
1. Eliminating Air Gaps
The primary reason thermal pads improve heat dissipation is their ability to conform to surface irregularities. When compressed between components, the pad deforms and fills gaps that would otherwise trap air. This significantly reduces thermal resistance at the interface.
Lower thermal resistance means heat moves more efficiently from the heat source to the cooling structure, preventing localized overheating.
2. Providing Consistent Thermal Contact
Unlike thermal pastes, which can be applied unevenly or dry out over time, thermal pads provide a consistent thickness and coverage area. This makes thermal performance more predictable, especially in mass production environments.
For manufacturers, consistency is critical. Using thermal pads reduces variation between units and simplifies quality control during assembly.
3. Supporting Mechanical Stability
Many thermal pads also act as mechanical cushions. They absorb vibration, accommodate tolerance differences, and reduce stress on fragile components. This is especially important in automotive electronics, industrial control systems, and portable devices that experience movement or shock.
Thermal pads reinforced with fiberglass, such as those used in high-load or vertical installations, maintain shape under compression and resist tearing during assembly.
Key Materials and Structures in Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are engineered using different material formulations to match specific thermal and mechanical requirements.
-
Silicone-based matrices offer flexibility, durability, and resistance to aging.
-
Ceramic or metal oxide fillers enhance thermal conductivity.
-
Fiberglass reinforcement improves tensile strength, tear resistance, and dimensional stability.

Thermal Pads vs Other Thermal Interface Materials
Thermal pads are one of several thermal interface material (TIM) options. Each has its advantages, but thermal pads are often chosen for their balance of performance and practicality.
-
Thermal paste offers high conductivity but can be messy, difficult to control, and prone to drying out.
-
Thermal grease performs well but is not ideal for automated assembly.
-
Thermal pads provide clean handling, repeatable thickness, and easy installation.
For many industrial and commercial products, thermal pads represent the most reliable and scalable solution.
Applications of Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are used across a wide range of industries and products, including:
-
Power modules and converters
-
LED lighting systems
-
Consumer electronics and communication devices
-
Automotive control units
-
Industrial power supplies
-
Battery packs and energy storage systems
In each of these applications, the thermal pad must match the operating temperature range, compression requirements, and electrical insulation needs.
Dubang Materials develops thermal pads with different hardness levels, conductivity values, and structural reinforcements to support these varied use cases.
Design Considerations When Selecting Thermal Pads
Choosing the right thermal pad involves more than just thermal conductivity. Engineers must also consider:
-
Pad thickness and compression ratio
-
Operating temperature range
-
Electrical insulation requirements
-
Long-term aging and reliability
-
Assembly process compatibility
For example, thicker pads may accommodate larger gaps but could introduce higher thermal resistance if not properly compressed. Reinforced pads may be necessary for vertical mounting or repeated assembly cycles.
Reliability and Long-Term Performance
Thermal pads are often expected to perform for many years without maintenance. High-quality materials resist pump-out, cracking, and hardening over time. Fiberglass-reinforced thermal pads are particularly effective in applications where mechanical integrity is critical.
By maintaining stable contact pressure and consistent thermal paths, these pads help protect components from thermal stress and premature failure.
Why Manufacturers Choose Dubang Materials
As thermal management requirements continue to evolve, manufacturers need suppliers that understand both material science and application realities. Dubang Materials focuses on producing thermal pads that combine:
-
Reliable thermal performance
-
Stable mechanical properties
-
Scalable manufacturing quality
-
Application-specific customization
This approach helps customers integrate thermal pads seamlessly into product designs without compromising reliability or assembly efficiency.
Conclusion
Thermal pads play a vital role in modern heat dissipation systems. By eliminating air gaps, ensuring consistent thermal contact, and supporting mechanical stability, they help electronic devices operate safely and efficiently.
As power densities increase and device designs become more compact, selecting the right thermal pad becomes a key engineering decision. With advanced material options and reinforced structures, thermal pads continue to be a practical and effective solution for long-term thermal management.
www.siliconethermal.com
Dubang